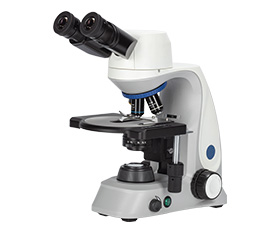
Pulmonary Tuberculosis Microscopy Instrument Solution
 What’s Pulmonary Tuberculosis
What’s Pulmonary Tuberculosis
Pulmonary tuberculosis, commonly called tuberculosis (TB), is a chronic infectious disease caused by the infection of lungs by Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. Pulmonary tuberculosis is the most common kind of tuberculosis. Typical pulmonary tuberculosis has a gradual onset and a long course. Common symptoms of pulmonary tuberculosis include slight fever, fatigue, anorexia, cough and hemoptysis, but most patients often have no obvious symptoms and are only discovered after X-ray examination, while some patients even go for examination and treatment after hemoptysis. Delayed diagnosis may increase the difficulty of treatment and the possibility of infecting others. If tuberculosis can be detected in time and treated appropriately, most cases can be clinically cured.
According to the World Health Organization, a total of 1.25 million people died from tuberculosis in 2023, including 161 000 people with HIV. Worldwide, TB has probably returned to be the world’s leading cause of death from a single infectious agent, following three years in which it was replaced by coronavirus disease (COVID-19). It was also the leading killer of people with HIV and a major cause of deaths related to antimicrobial resistance.
Diagnostic Methods for Pulmonary Tuberculosis
Clinical feature
Early pulmonary signs are usually not obvious. When the lesion spreads to a larger area, voiced sounds are shown in local percussion examination and tubular respiratory sounds can be heard on auscultation. When co-infection or bronchiectasis, moist rales can be heard.
Imaging examination
Chest X-ray examination can show the location and extent of lung lesions, the presence or size of cavities and the thickness of cavity walls. X-ray has different penetrability to various tuberculosis lesions. Through X-ray examination, the pathological nature of tuberculosis lesions can be approximated.
It must be pointed out that the symptoms, clinical features and imaging examination of pulmonary tuberculosis are similar to other chest diseases including non-tuberculous mycobacterial lung disease.
Laboratory examination
Bacteriology examination: Smear test is positive under microscope examination. Mycobacterium tuberculosis is positive.
Molecular biology examination: Nucleic acid test of mycobacterium tuberculosis is positive.
Pathology examination: Histopathological changes in tuberculosis.
Immunology examination: Tuberculin skin test is moderately positive or strongly positive. Interferon-γ release test shows positive.
Pulmonary Tuberculosis Microscopy Instrument Solution
Bacteriology examination
Detect whether there is mycobacterium in sputum samples by microscope observation for diagnosis of tuberculosis.
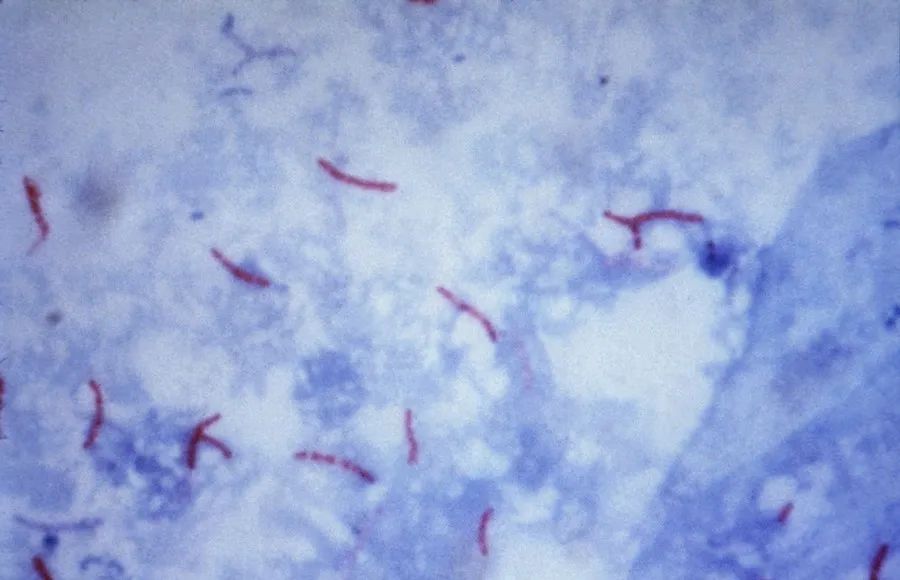
The Ziehl-Neelsen staining method
Different dyes can be used for staining of mycobacterium for microscopy observation, but they are all according to the fact that the cell membrane of mycobacterium contains more lipids, the main component of which is mycolic acid. Mycolic acid has acid resistance. After staining the mycobacterium with dyes, the cell membrane of mycobacterium can resist the decolorizing agents such as hydrochloric acid and ethanol, making the mycobacterium maintain the color of the dye. The Ziehl-Neelsen staining method, using carbolfuchsin to stain mycobacterium purple-red with heating the sample to promote the binding of the dye to the cells. After acidic alcohol decolorization, acid-resistant bacteria maintain the purple-red color, while other shed cells or non-acid-resistant bacteria are decolored and then counterstained blue with methylene blue as a dyeing agent. Observe with optical biological microscopes in bright field, purple-red rod-shaped acid-resistant bacteria can be seen against a blue background.
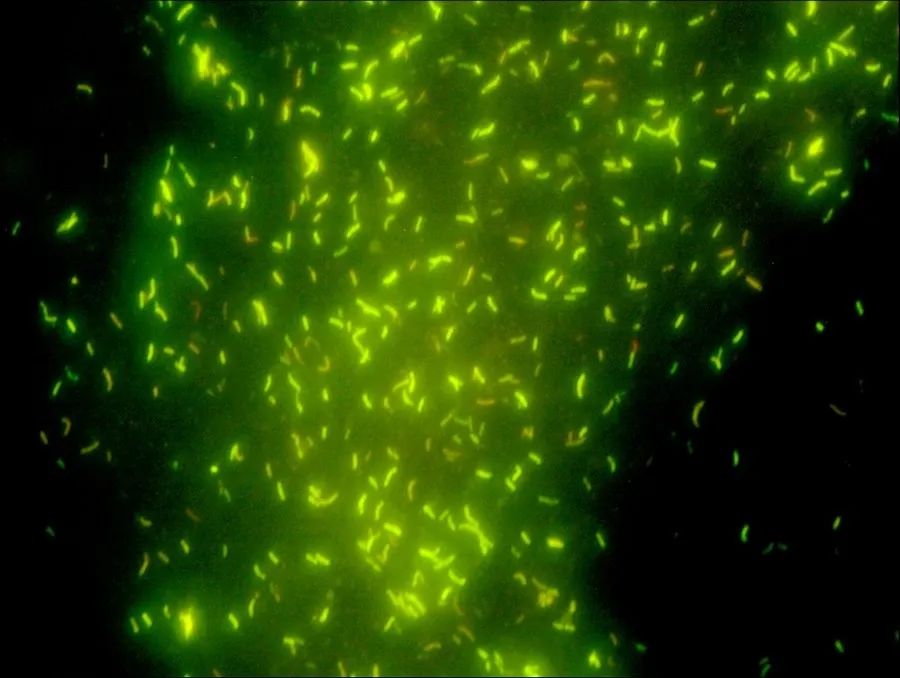
The Auramine-O fluorescent staining method
The mycobacterium emits an orange-yellow color under the fluorescence microscope with a UV light source after being stained with Auramine-O dye. It shows yellow-green fluorescence at high magnification, such as 40X objective and 10X eyepiece, appearing rod-shaped or branched.
Pathology examination
Detect whether there are histopathological changes in tuberculosis in the diseased part by microscope observation for diagnosis of tuberculosis.
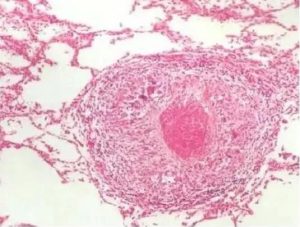
Observing the pathological characteristics of lesions
The pathological lesions are characterized by epithelium granulomatous inflammation. Under bright field of optical microscopy, varying sizes and quantities of necrotic and non-necrotic granulomas can be seen. Granulomas are formed by the fusion of epithelioid cell nodules. Typical tuberculosis lesions consist of confluent epithelioid cell nodules, with caseous necrosis at the center, multinucleated Langhans giant cells around and lymphocyte infiltration and proliferating fibrous connective tissue on the outer layer. If using Ziehl-Neelsen staining method, there is red stained short rod-shaped bacteria with blunt and slightly curved ends under bright field of microscope in the center of the necrotic area or at the junction of the junction of the necrotic area and the epithelioid granuloma. If using Auramine-O fluorescent staining, bacteria can be seen under fluorescent microscope.
Puncture smear examination
Puncture smear examination is a commonly used method in clinical practice, which is simple to operate and the result is relatively reliable. Use a fine needle to puncture and extract a small amount of body fluid and cells as sample of the diseased part. Then use the Ziehl-Neelsen staining method to stain the sample. Under the bright field of microscope, acid-resistant bacteria can be seen.
In conclusion, tuberculosis usually can be detect with Ziehl-Neelsen-Staining or fluorescence excitation, e.g. with Auramine O dye, so a fluorescent biological microscope is an ideal choice which can simply switch between the two modes.
Recommended Fluorescence Microscope
BS-2036F2(LED, TB) Fluorescent Biological Microscope
BS-2044F(LED) LED Fluorescent Biological Microscope
BS-2047F Fluorescent Biological Microscope
BS-2048F Fluorescent Biological Microscope
BS-2063F2(LED, TB) LED Fluorescence Microscope
Microscopy scanning system
If many slides need to be detected, the traditional microscope examination will meet following prolblems: low efficiency, high undetected rate, big difference in diagnosis, difficult referral, sharing data cannot be saved, high work intensity and many other defects. To solve it, automated equipment is needed.
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Microscopy Scanning System with fluorescence module, Auramine O, can automatically acquire and preserve sputum smear image acquisition, intelligent recognition analysis and processing the image, combined with advanced artificial intelligence algorithm, the equipment give negative and positive grade to determine the sputum smear.
Recommended Microscopy Scanning System
Scanpro3 Series Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Microscopy Scanning System
Recommended Microscope Digital Camera
BUC5F Series C-mount USB3.0 CMOS Camera (HISPVP)
BUC5IB Series Cooled C-mount USB3.0 CMOS Camera
BWHC4-4K Series HDMI/NETWORK/USB Multi-outputs C-mount CMOS Camera
BWHC4-4KAF8MPA HDMI/WiFi/USB Multi-outputs C-mount CMOS Camera