What are the classifications of microscope objectives?
 Objective lens is the most important optical component of microscope. It is composed of several lenses to overcome the imaging defect of single lens and improve the optical quality of objective lens. The quality of objective lens is the primary criterion to measure the quality of a microscope.
Objective lens is the most important optical component of microscope. It is composed of several lenses to overcome the imaging defect of single lens and improve the optical quality of objective lens. The quality of objective lens is the primary criterion to measure the quality of a microscope.
The structure of objective lens is complex and the production is precise. It involves two important factors: parfocal and concentric. Parfocal means that in the microscopic examination, when the image is clearly observed with a certain magnification objective lens, the imaging should be basically clear when the objective lens is converted to another magnification. In the above operation, the center deviation of the image should also be within a certain range. Parfocal performance and concentric degree is an important indicator of microscope quality, which is related to the quality of the objective lens itself and the accuracy of the objective converter.
There are many kinds of objective lenses, which can be classified from different regulations:
Regulation1: Chromatic Aberration Correction
1. Achromatic: An achromatic is commonly used in laboratories and often have the word “Ach” on its case. It corrects vertical chromatic aberrations for both blue (486nm) and red (656nm) wavelengths, and also corrects spherical aberrations for light at 546nm. It can not correct the chromatic aberration and spherical aberration of other colors, and the field curvature is very large. It is often used in medium and low level microscopes.
2. Apochromatic: The structure of the apochromatic objective lens is complex, which is made of special glass or fluorite and other materials. The shell of the objective lens is marked with the word “Apo”. This objective lens can not only correct the chromatic aberration of red, green and blue light, but also correct the spherical aberration of red and blue light. Due to the perfect correction of various aberrations, it has a larger numerical aperture than the achromatic objective of the corresponding magnification, which not only has high resolution, excellent image quality, but also has a higher effective magnification. As a result, apochromatic objectives have high performance. They are suitable for advanced research microscopy and photomicrography.
3. Semi-apochromatic: Semi-apochromatic objective is also known as fluorite objective. The shell of the objective is usually marked “FL”. In terms of structure, the number of lenses is more than that of achromatic objectives, but less than that of apochromatic objectives. In terms of the degree of aberration correction, semi-apochromatic objectives are between achromatic and apochromatic. For other optical properties they are close to apochromatic objectives. Its price is relatively low, so that it is often used to replace apochromatic objectives. It is best to use it in conjunction with compensating eyepieces. It can also be used for fluorescence observation. It is a relatively advanced objective lens.
Regulation2: Flatness of Aberration
The plan objective lens is to add a meniscus thick lens to the lens system of the objective lens to achieve the purpose of correcting the defects of field curvature and improving the imaging quality at the edge of the field of view. The flat field of view of the plan objective lens is more suitable for microscopy and photomicrography.
 1. Plan achromatic: “Plan” is marked on the shell of the objective. It adopts a complex structure of multi-lens combination, which effectively corrects astigmatism and field curvature, and overcomes the problem of uneven field of view of the achromatic objective. Plan achromatic objective still has residual chromatic aberration, if its vertical axis chromatic aberration is below 1%, it can be used without chromatic aberration correction compensation eyepiece; if vertical axis chromatic aberration is above 1% and below 2.5%, it needs to be used with compensation eyepiece use.
1. Plan achromatic: “Plan” is marked on the shell of the objective. It adopts a complex structure of multi-lens combination, which effectively corrects astigmatism and field curvature, and overcomes the problem of uneven field of view of the achromatic objective. Plan achromatic objective still has residual chromatic aberration, if its vertical axis chromatic aberration is below 1%, it can be used without chromatic aberration correction compensation eyepiece; if vertical axis chromatic aberration is above 1% and below 2.5%, it needs to be used with compensation eyepiece use.
2. Semi-plan achromatic: Semi-plan objectives have an 80% flat field. They can either be two lens element achromats or three or more element apochromats. They also can offer a very good quality of image.

3. Plan Apochromatic: The “Plan Apo” is engraved on the shell. Plan apochromatic objectives have the same degree of aberration correction as apochromatic objectives, except for further correction of field curvature. Imaging with apochromatic objectives is not as flat as achromatic objectives, while plan apochromatic objectives can make images clear and flat, further improving imaging quality.
 4. Semi-plan apochromatic: “Plan FL” is usually engraved on the shell of the plan semi-apochromatic objective. The achromatic performance is between that of the plan achromatic objective and the plan apochromatic objective. Fluorite (CaF2) material is generally used, also known as fluorite objective.
4. Semi-plan apochromatic: “Plan FL” is usually engraved on the shell of the plan semi-apochromatic objective. The achromatic performance is between that of the plan achromatic objective and the plan apochromatic objective. Fluorite (CaF2) material is generally used, also known as fluorite objective.
Plan objectives also have more advanced super-plan objectives (S Plan engraved on the shell) and super-plan apochromatic objectives (S Plan Apo engraved on the shell).
Regulation3: Function
1. Phase contrast objective: It is used to observe colorless and transparent specimens or living cells with inverted microscopes. Generally the font is green with a PH logo. It can also be used in conjunction with a phase contrast condenser on an upright microscope.
2. DIC objective: Generally, a semi-apochromatic or apochromatic objective lens is required, which is used for DIC microscopy to observe colorless samples or cells, and the image presents a three-dimensional effect.
3. HMC objective: It is marked with the HMC logo. It is similar to the phase contrast objective lens. Observation effect stereo sense is strong, but it cannot be used for fluorescence observation. These objectives are typically used with Hoffman phase contrast accessories.
4. Polarized objective: It is marked with the word POL. The assembly of this objective lens is stress-relieved, and it is specially designed for polarized observation.
5. Multifunctional objective: Some manufacturers produce a multifunctional objective, such as phase contrast, DIC, fluorescence, etc.. This objective is slightly more expensive. They often carry the “U” logo, such as Olympus’s “UPLFLN” and Zeiss’s “EC PLAN — NEOFLUAR” series objective.
Regulation4: Special Objectives
1. Objective lens with correction ring: There is an annular adjustment ring in the middle of the objective lens. When the adjustment ring is rotated, the distance between the lens groups in the objective lens can be adjusted, so as to correct the coverage difference caused by the non-standard thickness of the cover glass. The adjustment ring of the objective lens housing is marked with numbers “11~23”, indicating that the error between the thickness of the cover glass of 0.11~0.23mm can be corrected.
2. Objective lens with iris diaphragm: An iris diaphragm is installed in the upper part of the objective lens barrel, and there is also a rotatable adjustment ring outside, which can adjust the size of the diaphragm aperture when rotating. The objective lens of this structure is an advanced oil immersion objective lens, which is often used for dark field observation. During the dark field microscope inspection, the illumination light often enters the objective lens due to some reasons, so that the background of the field of view is not dark enough, resulting in a decline in the quality of the microscope inspection. At this time, adjust the size of the diaphragm to make the background darker and the inspected object brighter to enhance the microscope inspection effect.
3. Objective lens without cover glass: Some objects to be inspected, such as smear films, etc., cannot be covered with a cover glass, and an objective lens without cover glass correction should be used during microscopic inspection. Otherwise, the image quality will be significantly degraded, especially in high magnification microscopy. The shell of this kind of objective lens is often marked with “NC”, and there is no “0.17” in the position marking the thickness of the cover glass, but “0” is marked.
Regulation5: Optical System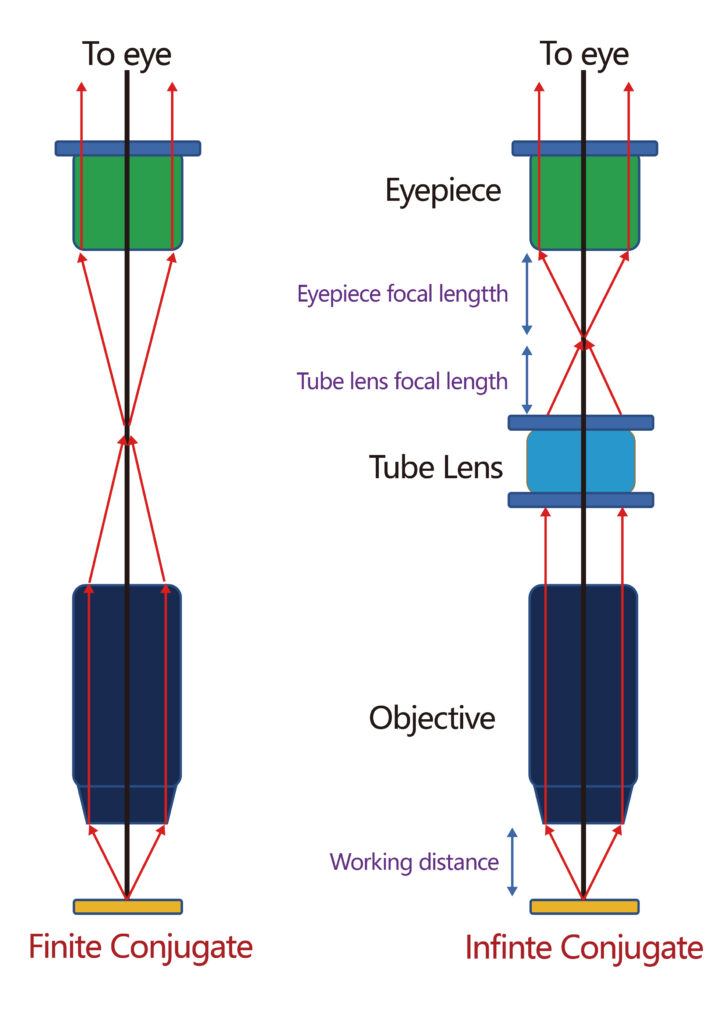
According to the optical system objective lens can be divided into finite-corrected objective lens and infinity-corrected objective lens. An infinity-corrected objective is a system where a light beam coming from a specimen goes through the objective lens (and does not create an image) and comes out as an infinity parallel beam through the tube lens which then creates an intermediate image. Infinity-corrected objective lenses are the industry standard now.
Regulation6: Manufacturers of microscope
According to the manufacturer, objective can be divided into Olympus objective, Nikon objective, Leica objective, Zeiss objective and so on. Here are some common objective lenses from different manufacturers.
Olympus UIS: It was introduced in 1993. Mainly used in AX, BX and CX and IX series.
Nikon CFI60: The Nikon CFI60 infinity-corrected brightfield objective, with a 60mm parfocal length and a thicker diameter, provides high brightness, working distance, and numerical aperture NA (gathering power).This objective is designed to correct for lateral and axial chromatic aberration over the entire field of view, resulting in high contrast and high-resolution images.
Leica HI PLAN: HI PLAN objectives provide excellent chromatic aberration correction in both wavelength ranges and ensure flatness over the entire field of view. Even the edges of the image are sharp without refocusing. HI PLAN objectives have fields of view (OFN) up to 25 mm and are available in phase contrast models. HI PLAN objectives offer excellent correction performance at a very cost-effective price.

ZEISS A-Plan Objectives: ZEISS A-Plan objectives offer a good performance for brightfield and fluorescence applications. It features excellent color correction and field smoothness, and is available with an oil immersion option for primary microscopy imaging.
The following table is the objective lens parameters of each brand to help you choose BestScope objective lens better.
Tube length of different brands
|
Microscope Brand |
Tube lens Focal Length(mm) |
Parfocal Distance (mm) |
Thread Type |
|
Leica |
200 |
45 |
M25 |
|
Nikon |
200 |
45/60 |
M25 |
|
Olympus |
180 |
45 |
RMS |
|
Zeiss |
165 |
45 |
RMS |
|
BestScope |
180/200 |
45/60 |
RMS/ M25 |
Note:
RMS and M25 is the thread size of the microscope objective and nosepiece.
RMS is 0.800”X1/36”(Diameter 20.32mm x thread pitch 0.706mm)
M25X0.75(Diameter 25mm x thread pitch 0.75mm)
Regulation7: Others
1. Classified by working distance
(1) Ordinary objective lens: the working distance is small, so slides can be observed but petri dishes cannot be observed.
(2) Long working distance objective: Generally with the “LWD” sign, it is the special objective lens for inverted microscope. It is designed and manufactured to meet the microscopic inspection of tissue culture, suspension and other materials. As such objects are placed in petri dishes or culture bottles, it is necessary to require a long working distance of the objective lens to meet the requirements of microscopic examination. The working distance is up to 10.6mm and can be optically corrected. It is suitable for 0~2mm thick glass and is usually corrected by correction ring or special glass cap. Examples include Olympus’s Luc PlFLN-PH objective and Zeiss’s LD-A-Plan PH objective.
2. Classified by medium between the front lens of the objective lens and the cover glass
(1) Dry system objective lens: During microscopic examination, air (n=1) is used as the medium between the front lens of the objective lens and the cover glass. This kind of objective lens is most commonly used, such as the objective lens below 40×, the numerical aperture is less than 1.
(2) Water-immersion objective lens: Generally marked with “W”, these water-immersion objective lenses are mainly used in physiology together with upright microscope, such as brain slices and the observation of thick samples. During microscopic examination, water is used as the medium between the front lens of the objective lens and the cover glass, so distilled water or normal saline should be used.
(3) Oil-immersion objective lens: Its magnification is 40×~100×. During microscopic examination, cedar oil and non-fluorescent oil (n=1.515 or so) were often used as media between the front lens of the objective lens and the cover glass. Sometimes glycerin (n=1.450), paraffin oil (n=1.471) as the medium. This type of objective is inscribed with the words “OIL” or “HI” on its shell.
The above-mentioned water-immersion and oil-immersion objective lenses are also known as “immersion objective lens” because the media used are all liquid substances, and the numerical aperture is greater than 1.
3. Classification by magnification
Extremely low power objective: This type of objective is designed and manufactured to view larger objects in full view, rather than magnifying. Some research microscopes are equipped with this type of objective lens, which should be used in conjunction with an extremely low magnification condenser lens during microscopic examination. Such as 0.75×, 0.5× objective lens.
Low power objective: 1×~6×, NA 0.04~0.15.
Medium power objective: 6×~25×, NA 0.15~0.40.
High power objective: 25×~63×, NA 0.35~0.95.
Oil-immersion objective: 40×~100×, NA 1.25~1.40.